OKLAHOMA CITY – Health officials are warning lake goers about a deadly amoeba that killed an Oklahoma swimmer this week.
Officials with the Oklahoma Department of Health say a person was hospitalized after swimming in Lake Murray last week.
Tragically, the victim died on Wednesday at an Oklahoma City hospital.
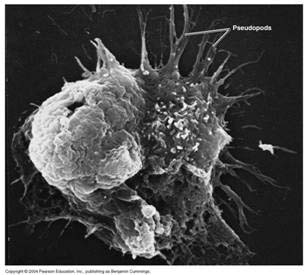
The Naegleria fowleri amoeba are often found in warm bodies of fresh water, including lakes and rivers.
“These disease-causing organisms are naturally present in most lakes, ponds, and rivers but multiply rapidly in very warm and stagnant water. Persons may be exposed to Naegleria fowleri amoeba when they dive or submerge their head in contaminated water. The amoeba then travels up the nose to the brain where it destroys the brain tissue,” a news release stated.
Experts say swimmers should take precautions to keep water out of their nose when swimming in unchlorinated bodies of water.
- Avoid forcing water up the nose when in bodies of fresh water.
- Hold your nose or use nose plugs when jumping or diving into water.
- Never swim in stagnant water, water that is cloudy and green, water that has mats of algae or water that has a foul odor.
- Do not swim in areas posted as “No Swimming.”
- Avoid swallowing water from rivers, lakes, streams, or stock ponds.
- Swimming in properly maintained pools prevents PAM because chlorine rapidly kills the amoeba.
Symptoms of PAM include high fever, headache, nausea and vomiting. Later, symptoms may include stiff neck, seizures, hallucinations and coma.
See a mistake? Report a typo here.